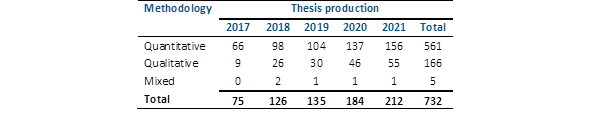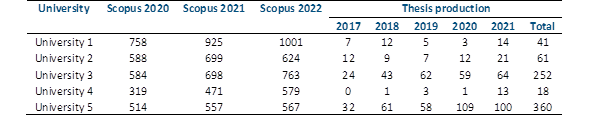Introduction
Psychological research lines of inquiry and problems are developed based on the researchers’ professional identities, lenses and experiences1. These have been systematized by the American Psychological Association (APA) in 54 divisions that represent either sub disciplines of psychology or topical areas that are further developed through research done by members and professionals affiliated to APA2. These divisions illustrate a wide variety of potential research topics based on novel, disruptive and high-impact psychological variables and categories in the academic community. In a recent study on the trends of psychological research from 1995 to 20153, a tendency of research topics associated with cognitive science, addiction and mental disorders, life satisfaction and motivation has been found. In addition, addiction interventions, spatial recognition, brain imaging techniques, regression models, chronic illnesses and quality of life, obsessive compulsive disorder, autism, smoking behavior and facial recognition are gaining momentum. In contrast, the study found that topics such as psychoanalysis, memory loss disorders, quantitative methods (validity), animal experiments (diet) and animal testing demonstrate a relative decline.
Psychological research can be developed by researchers and also by undergraduate or postgraduate students. In an undergraduate level, psychological research is specially challenging due to the limited ability of students to develop coherent and logical research problems and methodological approaches4. Moreover, in Latin America, although research is recognized as important, it is not yet considered as a means for economical and socio-political development5, so its implementation is still in progress6. This challenge is not different in Peru, where the defense of an undergraduate thesis is a prerequisite for professional practice. For this reason, students need to prepare a research project during their stay at the university, in order to be able to defend it right after graduation7. This is part of the formative research program offered by universities in order to not only develop publishable research, but also to develop research competencies in students. Nevertheless, this process is carried out in a context in which the culture of research is not yet established among mental health professionals8.
For Peruvian undergraduate students, this constitutes an issue, since students tend to avoid writing a thesis due to psychological, circumstantial, familial, university, social and cultural factors9. When the student is determined to overcome such barriers and develop a thesis, the university plays an important role in promoting research topics that are socially relevant. According to the national policy for the development of science, technology and technological innovation 10), if this is not the case, research topics and research results may not be congruent with the needs of the public and private sectors.
The analysis on Peruvian psychological research trends has been systematized in publications that address discipline-specific research topics such as blended learning11, educational psychology12, cyberbullying13, among others. In the context of research done by undergraduate students, Mamani-Benito14 states that most of the analyzed thesis demonstrate a good or regular quality. The same study reports that Peruvian research tends to follow lines of inquiry such as positive psychology, clinical psychology, educational psychology, social psychology, organizational psychology and psychometrics. In general, a more succinct and profound analysis of psychological research trends has not yet been developed.
Therefore, in order to describe the nature of research orientations of Peruvian undergraduate psychology students, the objective of this study is to identify the main research trends in undergraduate psychological theses from Peruvian universities. As a specific objective, quantitative and qualitative research design trends will be distinguished.
Methods
Research Design
A descriptive and retrospective systematic review of psychological research thesis of Peruvian undergraduate students was conducted. Data extraction was mediated by the following eligibility criteria: (a) Open Access theses published from 2017 to 2021, (b) published by undergraduate students of the top five universities ranked by Scopus University Rankings and (c) allocated in institutional repositories and in the Peruvian National Registry of Research Works (RENATI). Studies that didn’t indicate the design either in the abstract or in the method section, and studies presented as state of the art of a particular topic were excluded.
Proceedings
Regarding the search process, first, a search protocol was created, which considered document elements such as the authors, year of publication, authors’ sex, title of the thesis, variables, type of sample, sample size, methodology, research design and university. The researchers conducted the data extraction process starting with RENATI database for an initial screening phase. This phase allowed a preliminary review of the general sample size. Since some theses couldn’t be accessed through RENATI, a second screening phase was conducted using the institutions' repositories of the five selected universities. Each thesis was screened by abstract and, if the information required by the search protocol was not clearly reported, the whole thesis was downloaded and revised, focusing mainly on the method section. This second screening process allowed the establishment of the specific sample sizes for each institution. The information of each thesis was recorded in a Microsoft Excel database.
Data analysis was conducted in two phases. First, data was organized in relation to its frequency of the categories of authors' sex, the universities were catalogued as universities 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 according to their ranking, the categories of years of publication, number of authors, designs, type of methodology, and area of publication were obtained. Descriptive frequency statistics were established based on these categories. Contingency tables were also used to evaluate frequencies according to other categories of variables15. In addition, the information obtained from the Scopus Web (https://www.scopus.com/home.uri) was used to attain the frequency of scientific production by year
The second phase of the analysis focused on the variables reported in each thesis in order to identify and organize research trends. For this purpose, lexicometric and statistical textual analysis16 were used through IRAMUTEQ (Interface Interface de R pour les Analyses Multidimensionnelles de Textes et de Questionnaires) version 0.7 Alpha217. This software identifies regularities within a text corpus by grouping statistically significant words based on their co-occurrence in the corpus18.
The analytical process was conducted by the following steps; First, the database was screened, reviewed, corrected and organized into a monothematic corpus, considering only the information related to the research variables reported in the title of each thesis. The information of each thesis was separated by a command line and associated to three variables in relation to the specific objectives of the study: year, topic and methodology (e.g., ***** *an_2017 *tem_org *met_cuant Clima Laboral Compromiso Organizacional). This process was carried out by using LibreOffice Calc software. The file was saved as a text document using UTF-8 standard encoding (Unicode Transformation Format 8-bit codeunits). The total number of text segments included in the analysis was 732. Next, a basic lexicography was applied to lemmatize the whole corpus using a default spanish dictionary. Then the word frequency was established, focusing on the active forms (i.e., verbs, nouns, adjectives and adverbs). The active forms with a frequency greater than the mean (M= 4.078) were selected for further analysis to reduce the extension of the corpus. Next, a specificities analysis was conducted, which helped reveal the association between each variable (i.e., topic and methodology) and the selected active forms. Hypergeometric Law index was used to establish the relation between the text segments and the variable, by which a higher value of the index explains a greater relation with the group.
Every thesis included in the study is public domain and available in its respective repository, so an approval of an IRB was not necessary. The study did not obtain data from humans; Therefore, it did not need to undergo an evaluation by an ethics committee.
Results
Descriptive Statistical Analysis
As shown in Table 1, on more than one occasion the research papers had more than one author; 82.3% were male and 17.7% were female. In relation to the universities, it was observed that University 5 has the highest thesis production (49.2%) together with university 3 (34.4%). Among all the universities, the year with the highest thesis production was 2021 (29.0%). Most of the works were single-authored (86.6%) and single-design (98.4%). At the same time, different quantitative (76.6%), qualitative (22.7%) and mixed (0.7%) methodologies were used. Finally, most of the topics were focused on clinical psychology variables (58.7%), with topics in social (10.8%), organizational (10.5%) and educational (10.1%) psychology being the next most frequent.
Overall, thesis production has witnessed an increase in both quantitative and qualitative studies from 2017 to 2021. However, the number of mixed studies were lower in recent years (Table 2).
On the other hand, a specific analysis of the production by universities compared to their production in Scopus shows that University 5 and 3 show a higher production of theses and, in turn, an increase in scientific production in Scopus. Unlike University 2, which has a lower thesis production than its scientific production, also, its scientific production in 2022 was reduced compared to 2021. However, University 1 and 4 have an exponential increase in their scientific production while their thesis production is low (Table 3).
Likewise, the topics that have shown an increase in theses have focused on clinical psychology, which has had a considerable increase in recent years (Figure 1). Another topic was social psychology, which has doubled the number of theses in recent years. Psychometric and educational studies have also increased. However, organizational studies, in the last year, decreased the number of topics in this area. On the other hand, sports psychology topics have increased in recent years, showing an interest in topics related to sports.
Exploratory Statistical Analysis
After the lemmatization, the analysis of the 732 text segments resulted in a total of 227 active forms. The following word cloud illustrates the frequency of the active forms (verbs, nouns, adjectives and adverbs), the highest being ‘social’ (social) (n = 72), ‘emocional’ (emotional) (n = 70), ‘afrontamiento’ (n = 61), ‘estilo’ (style) (n = 61), ‘Stress’ (n = 54), ‘psicológico’ (psychological) (n = 51), ‘bienestar’ (wellbeing) (n = 48), etc. Frequencies show that, in general, Peruvian psychological research tends to study variables such as coping styles (social and emotional), satisfaction, wellbeing, psychological stress and work stress (Figure 2).
Specificities Analysis
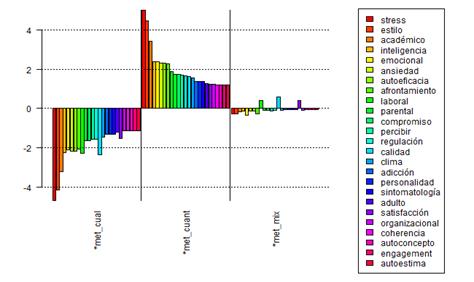
A specificities analysis was conducted on the active forms, which organized the list in relation to two main variables: Methodology and research topic. With respect to methodology, the analysis shows that thesis which report a qualitative methodology tend to focus on open and abstract variables such as representation, experience, process, construction, configuration, subjectivity and belief. In relation to more specific variables, maternity, paternity, grief, femininity, and masculinity appear to be the most frequent. Figure 3 presents the first 25 forms with a higher index (≥ 1,6967) for illustrative purposes.
With regards to quantitative research, the analysis shows that thesis with a quantitative methodology tend to study variables such as stress, coping style, emotional intelligence, anxiety, self-efficacy, engagement, quality of life, addiction, organizational satisfaction, organizational climate, coherence, self-concept, engagement and self-esteem. Figure 3 also shows that some variables are used in mixed methods research, being work, quality and satisfaction in an organizational context. Figure 4 presents the first 25 forms with a higher index (≥ 1, 1976) for illustrative purposes.
With respect of research topics, data was first manually categorized in five branches of psychological research: clinical psychology, educational psychology, sports psychology forensic psychology, organizational psychology, social psychology and psychometrics. Then, by using a specificities analysis, trends were further categorized by means of the relative frequency of the forms, which better illustrates the differences and tendencies of the variables. The first 25 active forms with the highest frequency (≥ 20) within the corpus were selected to better illustrate their distribution between topics.
Figure 5 shows how the most frequent terms are organized in relation to psychological branches. In general, theses on clinical psychology tend to study variables such as coping styles, emotional coping, psychological wellbeing, stress, life satisfaction, attachment, intelligence, life quality, anxiety and resilience. Sports psychology research trends are related to psychological wellbeing, psychological satisfaction, resilience, motivation and self-efficacy. Other research topics that do not appear as frequent in the whole corpus but are specific to this branch are flow theory and goal orientation. Educational psychology research trends also focus on motivation, self-efficacy and stress from an academic point of view. More specifically, the term ‘académico’ (academic) is related to variables such as academic performance, academic resilience, academic stress and coping.
On the other hand, theses on forensic psychology focus on variables related to the term ‘familiar’ (familiar), such as family functioning, family social climate, family dynamics and family satisfaction. Also, some other topics that do not appear as frequent in the whole corpus but are specific to this branch are violence, fear, adaptability, etc. Thesis on organizational psychology are developed around topics such as satisfaction, engagement, motivation and leadership. The words ‘laboral’ (work) and ‘organizacional’ (organizational) are related to variables such as satisfaction, stress, climate, psychosocial factors and work conditions. Meanwhile, the main social psychology research topic is social representations. Other research topics that do not appear in Figure 4 but are frequent within this branch are identity, stereotypes, attitudes, gender, violence, etc. Finally, psychometrical theses revolve around topics such as attitude, anxiety, motivation, resilience and satisfaction. More specifically, it focuses on physical and psychological health, work related variables (e.g., performance, absenteeism), relationships and internet use.
Discussion
Scientific production can be expressed through articles in periodical and indexed journals, articles in non-indexed journals, and undergraduate and/or graduate theses19. Although, the 742 theses identified in the present study do not reliably express the number of sustained theses on psychology in Peruvian universities between 2017 to 2022, however, the number of theses recovered allows showing trends in the scientific production on psychology. Thus, the work aimed to analyze the lines of research on psychology from the theses developed that allow pointing out different aspects of the construction of scientific knowledge on psychology.
With respect to the thematic analysis of the papers, it is observed that they address a varied set of topics that cover different aspects of interest in psychological research in Peru, highlighting the works that deal with topics related to coping styles (social and emotional), satisfaction, well-being, psychological stress and work stress. This can also be observed if the thematic areas are analyzed according to qualitative or quantitative methodology. In this sense, the different topics are predominantly framed within the clinical and health psychology line of research. This, has also been seen in previous studies in Peru, where this line of research was the most frequent8.
A study on lines of research in Colombian universities also indicated that clinical psychology was one of the most investigated by different research groups20. This finding, regardless of the type of research, is important if one takes into consideration that the frequency of lines of research that include mental health as a priority of study in Peruvian universities is low8.
One study indicated that only 48% of research lines consider as a priority for study the factors associated with depression, violence, addictive behaviors, psychosis and dementia; 20% the state of negative and positive mental health; 4% the development of intersectoral strategies with cultural appropriateness, and another 4% the evaluation of prevention and promotion strategies in mental health with intersectoral participation8.
According to what was mentioned above, we find that Rey21, mentions that the research projects with the highest incidence were those related to the areas of clinical psychology and mental health such as: psychotherapy, psychopathology, abnormal behavior, psychotherapy, psychopathology, abnormal behavior. At the same time where they analyzed the trends in the lines of research in doctoral programs, coincides with our study where initially it is shown that Clinical Psychology is the area with the highest participation, as a second line mentions the variables related to cognitive processes and finally the line related to Health psychology22.
Likewise, an exponential increase of quantitative studies was observed in contrast to qualitative and mixed studies. These results can be understood that quantitative methodology in psychology has a greater presence within the subjects and competency training than qualitative and mixed studies. Although general inferences could not be made, the current situation of universities in terms of scientific production shows a tendency towards quantitative studies.
Another point of interest is that at the undergraduate level there are more women than men in the classroom. However, the production of these shows a different reality. On the one hand, this phenomenon can be explained by the fact that women prefer to study psychology because of their higher level of empathy and because it is a life-oriented field23. However, scientific production may show another picture, where men publish more than women in sensations and perceptions, neuroscience, clinical psychology and health; however, in developmental psychology women show greater presence24. These differences may be caused by multiple factors, but to mitigate this trend it is necessary to implement a set of strategies to reduce biases between male and female differences in scientific production25.
The study presented some limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, information was only obtained from theses submitted by the five best Peruvian universities classified by Scopus University Rankings that teach psychology. This left out other universities that also provide training in psychology, but are not within the indicated criteria. Second, it was not possible to analyze the possible causes for the presence of the different thematic areas of the undergraduate theses. This is due to the fact that only the available data was analyzed. It is suggested that the universities carry out future studies to investigate these possible causes and to see other possible influencing factors. Third, we were only able to review the theses that were available on the RENATI website, so future research should conduct a more detailed analysis and verify the theses by other means.
The present review study of undergraduate theses in Peru has allowed us to identify trends and thematic topics in the construction of scientific knowledge on psychology. Therefore, it has provided evidence that undergraduate research on psychology is a heterogeneous area of work. The results provide relevant information to improve the scientific production in psychology in our country. For this, it is necessary that universities design policies aimed at improving their scientific production and thematic diversity in psychology through the strengthening of the culture of publication and active participation of teachers and students26. It is suggested that, the different strategies incorporate discipline, reading research on related areas in psychology, teaching research by researching, teaching scientific writing as a collaborative process, teaching by example, disseminating information about lines of research, and achieving an adequate relationship between advisor and student in the research process19.