INTRODUCTION
It is imperative to acknowledge the paramount importance of mental health in everyday life, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, which has significantly affected the well-being of individuals1,2. Widespread isolation, economic uncertainty, and fear of illness have exacerbated these effects3-5. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct an analysis of news articles to examine how mental health information has been disseminated, which topics have been most frequently addressed, and how the discourse surrounding mental health in Paraguay has been constructed.
The dissemination of information and news reporting on mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic played a pivotal role in shaping public opinion, perception, and comprehension of mental health issues. Consequently, it is important to scrutinize the process of selecting information sources and crafting news stories in this domain to evaluate the reliability and credibility of media coverage.
The decision to analyze the attributes of news sources and newsrooms is driven by the imperative to comprehend the caliber and reliability of the intelligence that has been disseminated to the public6,7. The year of publication and the author's gender plays a critical role in evaluating the timeliness and credibility of the sources. Furthermore, a thorough examination of writing characteristics, such as the type of grammar, context, connotation, and topic of the article, is crucial in identifying patterns in the manner mental health-related information is portrayed8.
The relationship between the characteristics of news sources and the connotation of mental health-related articles in Paraguay during the COVID-19 pandemic years 2020-2023, played a crucial role in shaping public perceptions of mental health9. The connotation of news articles can significantly influence audience perceptions of the severity of mental health issues as well as attitudes towards individuals affected by mental disorders10,11. Thus, the primary aim of this study was to examine the characteristics of mental health-related news in Paraguay during the pandemic to understand its potential impact on public perception.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Design and sampling
This was an observational, descriptive, retrospective study of prevalence and cross-association12,13. Non-probabilistic sampling was used in consecutive cases. All news articles containing information on mental health published in the three primary newspapers of the country (ABC Color, Última Hora, La Nación) between May 2020 and May 2023, within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic in Paraguay, were included. This study focused on identifying mentions of depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and mental health issues.
Data Collection
In our study, we collected all news articles published during the period under investigation and identified relevant sources of information containing the keywords "depression," "anxiety," "bipolar disorder," "schizophrenia," or "schizophrenic," "mental health," or "depressed," "anxiety disorder," "mental health awareness," or "mental illness."
Variables
The following variables were selected based on the work of Arneaud et al.14:
a. Characteristics of the news sources: Year of publication (2020, 2021, 2022, 2023), identification, and gender of the author (male, female).
b. Writing style: Type of grammar (first person, third person), context (criminal, educational, human interest, incidental reference, medical/scientific, metaphor), connotation (positive, negative, neutral), article topic (crime, death, death by suicide, economics/finance, education, environment, health and wellness, legal/justice, mental health awareness, politics, pop culture, social/family, sports), and health expert articles (yes, no).
The article's connotation was determined based on the subjective assessments of the researchers and the overall tone of the text concerning mental health disorders, consistent with similar studies14.
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted using the statistical package Jamovi version 2 and RStudio version 2023.09.0+463. Categorical variables were summarized in the tables and figures. A chi-square test with a significance level of 5% was used to determine the relationships between the variables. The dichotomized outcome variable was utilized in the chi-square model, grouping "positive connotation" and "neutral-negative connotation."
RESULTS
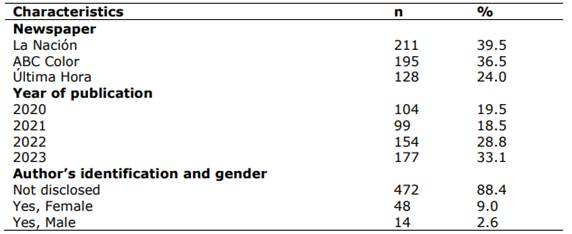
A total of 534 news articles on mental health were published between 2020 and 2023, 39.5% were issued by La Nación, 33.1% were published in 2023, and 88.4% of the news articles did not specify the gender of the author. Table 1
With regard to the writing style of the news articles, it was observed that 99.8% were written in third person, 62.7% were presented in a human-interest context, 48.5% had a neutral tone, 65.7% focused on health and well-being, and 7.5% were authored by a health expert (as shown in Table 2).
Table 2. Writing style of the news (N=534)
| Characteristics | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Type of grammar | ||
| Third person | 533 | 99.8 |
| First-person | 1 | 0.2 |
| Context | ||
| Metaphor | 6 | 1.1 |
| Educational | 19 | 3.6 |
| Medical/scientific | 30 | 5.6 |
| Incidental reference | 144 | 27 |
| Human interest | 335 | 62.7 |
| Connotation | ||
| Neutral | 259 | 48.5 |
| Positive | 93 | 17.4 |
| Negative | 182 | 34.1 |
| Article topic | ||
| Crime | 3 | 0.6 |
| Social/family | 3 | 0.6 |
| Economy/finance | 4 | 0.7 |
| Legal/justice | 6 | 1.1 |
| Environment | 7 | 1.3 |
| Death | 7 | 1.3 |
| Politics | 8 | 1.5 |
| Sports | 19 | 3.6 |
| Education | 31 | 5.8 |
| Pop culture | 31 | 5.8 |
| Awareness | 32 | 6.0 |
| Suicide | 32 | 6.0 |
| Health and wellness | 351 | 65.7 |
| Health expert author | ||
| Yes | 40 | 7,5 |
| No | 494 | 92,5 |
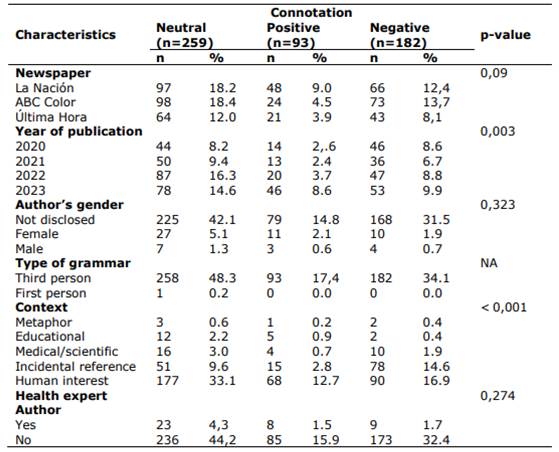
In the bivariate analysis, a statistically significant relationship was uncovered between the year of publication and connotation (χ2=19.6 gl=6 p=0.003) and with the context of publication (χ2=39.4 gl=8 p<0.001) (see Table 3 for details).
DISCUSSION
A thorough examination of news articles related to mental health in Paraguay from 2020 to 2023 was conducted. Our findings provide valuable insights into the communication of mental health news during the COVID-19 pandemic in Paraguay by highlighting several key aspects.
In total, 534 news items related to mental health were identified. This suggests a notable level of interest in and media coverage of the topic of paramount importance during the pandemic. Most of these were published in the La Nación newspaper. Furthermore, 2023 accounts for the highest number of news items, accounting for 33.1% of the total. This surge in coverage during the year 2023 might be attributed to a heightened public awareness of mental health issues due to the pandemic7,16.
A noteworthy observation concerning the attributes of the news articles was that in almost 90% of the cases, the identification and sex of the author were not specified. This is a persistent issue in Paraguayan publications, where the author's name is often not mentioned, which differs from most publications worldwide17. The lack of specification may suggest a deficiency in transparency regarding news authorship or a common practice in which the gender of the author is deemed irrelevant to the subject matter of the news item. However, it is imperative to recognize that the inclusion of author information can impart additional credibility and context to news stories18.
Considering the attributes of newswriting, several discernible patterns have emerged. The overwhelming majority of news accounts were conveyed in third person, indicating an objective approach to reporting, which is of utmost importance in ensuring accurate coverage of mental health18.
It is of note that most of the news stories, comprising more than half, were framed within the context of "human interest." This methodology is crucial for fostering an emotional connection with readers and emphasizing the significance of mental health within the realm of genuine human experiences. Furthermore, the fact that 65.7% of news stories targeted "health and wellness" issues underscores the valid concern for raising mental health awareness as an integral element of the overall well-being of the population. This contrasts with other studies where the news primarily focused on criminal activities14,19-21.
In terms of news connotations, 48.5% presented a neutral tone, which can be considered a balanced approach to mental health coverage, avoiding polarization, and promoting an accurate representation of mental health problems. Of the news articles, 34.1% had a negative connotation, which is less than that reported in a similar study 14.
Although only 7.5% of news items were penned by health experts, the incorporation of these voices can serve as a reliable foundation for mental health information and guidance. This is attributable to the limited number of mental health specialists in Paraguay22,23.
Bivariate analysis revealed a significant correlation between the connotation of news articles and both the year of publication and the context in which the news was written. This correlation may indicate a shift in the way mental health is portrayed over time, potentially reflecting the growing concern for mental health amidst the pandemic and its impact on public perception1.
When interpreting the results of this study, it is imperative to appreciate the significance of precise and impartial communication in mental health. Media can contribute significantly to raising consciousness and combating the stigma surrounding mental health disorders. The study's findings emphasize the necessity of increased transparency in news authorship and a fair and objective approach to reporting news stories related to mental health.