INTRODUCTION
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus emerged from Wuhan, China, leading to a respiratory disease later named COVID-191. Despite initial containment efforts, SARS-CoV-2 spread rapidly across multiple continents, prompting the World Health Organization to declare a pandemic on March 11, 20202. By April 2023, the virus had caused over 756 million confirmed cases worldwide5,6. Most infections present with mild symptoms, though approximately 20% of patients develop complications, and less than 5% require hospitalization for severe disease3, (4.
Several studies have identified chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs) as critical risk factors for severe COVID-19 outcomes, particularly in patients over 60 years2,7. Diabetes stands as one of the most frequent comorbidities, significantly increasing the risk of severe complications5-8. Studies have demonstrated that obesity correlates with disease severity, with risk increasing proportionally to body mass index9,10. Additionally, smokers show 1.4 times higher risk of severe COVID-19 and 2.4 times greater likelihood of ICU admission compared to non-smokers11.
While NCDs clearly influence COVID-19 severity, data from developing countries remains limited, where demographic characteristics and comorbidity patterns differ substantially6. In Paraguay, the first death and community transmission case were confirmed on March 20, 2020, initiating nationwide quarantine measures12. By September 2023, the country had reported 813,163 cases, 62,251 hospitalizations, and 19,970 deaths13. Understanding local patterns of disease interaction becomes crucial for healthcare planning, particularly in resource-limited settings.
This study aims to describe the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 patients hospitalized during the pandemic's first seven months in Paraguay, with particular focus on NCD impact. Our analysis examines records from five major referral hospitals to identify risk factors for severe disease and mortality. These findings will help establish evidence-based protocols for managing high-risk patients in similar healthcare contexts. We hypothesize that the presence and number of NCDs significantly influence COVID-19 outcomes in our population.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We conducted a descriptive cross-sectional analytical study analyzing medical records of patients hospitalized with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. The study included five major COVID-19 referral centers authorized by the Ministerio de Salud Pública y Bienestar Social (MSPYBS) in Paraguay: Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias y del Ambiente-Juan Max Boettner (INERAM), Clínica Periférica IPS-INGAVI, Hospital Geriátrico Buongermini-IPS, Hospital Nacional de Itauguá (HNI), and Hospital Respiratorio Integrado IPS-MSPBS del Alto Paraná. These centers were selected based on their high complexity level and designation as respiratory disease referral facilities.
The study period extended from the first confirmed case on March 7, 2020 (epidemiological week 10) through September 5, 2020 (epidemiological week 36). We included only patients with complete medical discharge records or death certificates and laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by RT-PCR. Cases lacking confirmatory diagnosis or missing essential variables were excluded from analysis.
Data collection followed a standardized protocol examining sociodemographic characteristics, clinical features, and outcomes. Sociodemographic variables included age (categorized as 0-19, 20-39, 40-59, 60-79, ≥80 years) and sex. Risk factors encompassed smoking, dyslipidemia, obesity, and alcohol consumption. We documented chronic diseases including type 1 and 2 diabetes, cardiovascular conditions (hypertension, stroke, acute myocardial infarction, heart failure), chronic respiratory diseases (COPD, asthma), and cancer. The total number of NCDs per patient was also recorded.
Hospital course variables included admission type (general ward or intensive care unit), use of mechanical ventilation, and outcome (medical discharge or death). Trained research staff accessed medical records at each facility, following strict data confidentiality protocols. All data were coded and entered into a database using Excel 2018®.
Statistical analysis employed EPI INFO version 7.1TM, beginning with descriptive statistics including absolute counts, frequencies, and proportions. We conducted binary bivariate logistic regression to identify potential predictors, followed by multivariate logistic regression using the Likelihood Ratio criterion. The primary outcomes were ICU admission and death, with p<0.05 considered statistically significant. For age comparisons, we used the 20-39 years group as reference. The number of NCDs was categorized as none, one, two, or three or more conditions.
This study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki principles for medical research using secondary data. Patient confidentiality was protected through data anonymization using coding systems, secure database encryption, and restricted access to identifiable information. Authorization was obtained from the management of each service to access the clinical records and the signature of the researchers' confidentiality consent.
RESULTS
From March 7 to September 5, 2020, 1,690 patients were hospitalized with COVID-19 across the five referral hospitals in Paraguay. Of these, 797 (47.2%) met the inclusion criteria and were included in our analysis. The temporal distribution of hospitalizations showed a gradual increase from epidemiological week 10, with peak admissions occurring during weeks 32-34 (Graph 1).
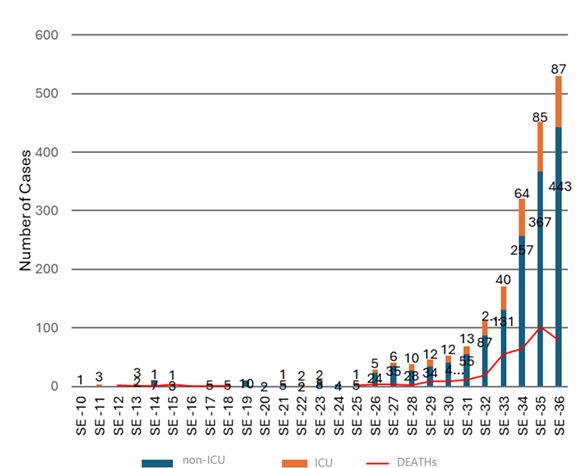
Sources: Epidemiological Report - Epidemiological Information Center/DGVS -MSPYBS). Prepared by the authors. From the patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 61.9% had some NCD, of which 28.9% had one NCD, 20.9% had two NCDs and 12% had three or more NCDs.
Graph 1 Hospitalized by COVID-19 according to type of hospitalization and deaths by epidemiological week from SE-10 to SE-36, Paraguay 2020.
The study population had a median age of 51 years, with one-third (33.3%) aged 60-79 years. Males comprised 53.8% of patients. Among hospitalized patients, 61.9% had at least one chronic non-communicable disease (NCD), and 24.9% presented with additional risk factors. Obesity was the most prevalent risk factor (12.8%), followed by dyslipidemia (11.9%). Nearly one-third (29.6%) of patients required ICU admission, and 17.6% needed mechanical ventilation. The overall mortality rate was 29.1%, while 70.8% of patients recovered and were discharged (Table 1).
Analysis of chronic disease patterns revealed that 28.9% of patients had one NCD, 20.9% had two NCDs, and 12.0% had three or more NCDs. Hypertension was the most common chronic condition (29.6%), followed by diabetes mellitus (25.6%), cardiovascular disease (16.4%), COPD (9.0%), and asthma (5.2%) (Table 1).
Table 1 Clinical characterization of patients hospitalized for COVID-19, 2020
| SEX | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Man | 429 | 53,83 | |
| Women | 368 | 46,17 | |
| Age Group | |||
| 19 years old and younger | 62 | 7,78 | |
| 20 to 39 years | 172 | 21,58 | |
| 40 to 59 years | 234 | 29,36 | |
| 60 to 79 years | 266 | 33,38 | |
| 80 years and more | 63 | 7,9 | |
| Pathological history | |||
| With chronic non-communicable diseases | 494 | 61,98 | |
| No chronic non-communicable diseases | 303 | 38,02 | |
| With risk factor | 199 | 24,97 | |
| No risk factor | 598 | 75,03 | |
| With a chronic non-communicable disease | 231 | 28,98 | |
| With two chronic non-communicable diseases | 167 | 20,95 | |
| With three or more non-communicable chronic diseases | 96 | 12,05 | |
| Risk factors | |||
| Alcohol consumption | 18 | 2,26 | |
| Smoking | 73 | 9,16 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 95 | 11,92 | |
| Obesity | 102 | 12,8 | |
| Chronic noncommunicable diseases | |||
| Hypertension | 236 | 29,61 | |
| Mellitus diabetes | 204 | 25,6 | |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 131 | 16,44 | |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 72 | 9,03 | |
| Cancer | 13 | 1,63 | |
| Asthma | 42 | 5,27 | |
| Type of hospitalization | |||
| Common hospitalization (non-ICU) | 561 | 70,39 | |
| Intensive care unit (ICU) | 236 | 29,61 | |
| Mechanical ventilation* | 141 | 17,69* | |
| Hospital discharge | |||
| Deceased | 232 | 29,11 | |
| Recovered | 565 | 70,89 | |
*The percentage shown is of the total number of ICU admissions.
Multivariate analysis identified several factors associated with ICU admission. Age showed a progressive increase in risk, from OR=1.78 for patients under 19 years to OR=3.01 for those over 80 years (compared to ages 20-39). The need for mechanical ventilation (OR=87.54, 95% CI: 36.49-210.00) and subsequent death (OR=8.10, 95% CI: 5.01-13.11) were strongly associated with ICU admission (Table 2).
Table 2 Determinants for ICU admission according to the final multivariate logistic regression (VR) model among patients hospitalized for COVID-19 with or without NCDs
| Variables | Odds ratio | IC 95% | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 19 years old / 20 to 39 years old | 1,78 | 0,9 | 3,54 | 0,045 |
| 40 to 59 years / 20 to 39 years | 2,23 | 1,38 | 3,6 | <0,001 |
| 60 to 79 years / 20 to 39 years | 2,8 | 1,76 | 4,47 | <0.,001 |
| 80 years and over / 20 to 39 years | 3,01 | 1,07 | 6,48 | 0,034 |
| MV* (Yes/No) | 87,54 | 36,49 | 210 | <0,001 |
| Deceased (Yes/No) | 8,1 | 5,01 | 13,11 | <0,001 |
| *MV: Mechanical Ventilation | ||||
Risk factors for mortality showed similar age-related patterns, with odds ratios increasing from 2.31 for ages 40-59 to 7.70 for those 80 and older (compared to ages 20-39). COPD (OR=2.58, 95% CI: 1.42-4.68) and ICU admission (OR=8.48, 95% CI: 5.20-13.85) significantly increased mortality risk. The presence of multiple NCDs also enhanced mortality risk, with OR=2.43 for two NCDs and OR=2.78 for three or more NCDs, compared to patients without chronic diseases (Table 3).
Table 3 Determinants of mortality by the final multivariate logistic regression (VR) model of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 with or without NCDs
| Variables | Odds ratio | IC 95% | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 to 59 years / 20 to 39 years | 2,31 | 1,22 | 4,36 | 0,009 |
| 60 to 79 years / 20 to 39 years | 4,65 | 2,52 | 8,61 | 0,000 |
| 80 years and over / 20 to 39 years | 7,7 | 3,45 | 17,16 | 0,000 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Yes/No) | 2,58 | 1,42 | 4,68 | 0,002 |
| Intensive care unit (ICU) (Yes/No) | 8,48 | 5,2 | 13,85 | 0,000 |
| MV* (Yes/No) | 2,41 | 1,36 | 4,26 | 0,002 |
| With two chronic non-communicable diseases/ no chronic non-communicable diseases | 2,43 | 1,61 | 3,69 | 0,000 |
| With three or more non-communicable chronic diseases/ no chronic non-communicable diseases | 2,78 | 1,7 | 4,54 | 0,000 |
*MV: Mechanical Ventilation.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is one of the few studies of the epidemiological profile of hospitalized patients in Paraguay showing the outcome of COVID-19 and associated risk factors. The importance of this study is its national representativeness, in terms of sample size and territorial coverage. This study has significant implications for public health with important findings on the relationship between COVID-19 and at-risk populations in Paraguay. The results of this study allow us to observe the situation of those hospitalized for COVID-19 and its severity associated with risk factors for admission to the ICU and death.
Our study provides one of the first comprehensive analyses of COVID-19 outcomes in Paraguay's healthcare system. The demographic profile of hospitalized patients mirrors findings from Espírito Santo, Brazil, particularly regarding male predominance and age distribution14. This similarity in patient characteristics across South American healthcare systems suggests common regional patterns in COVID-19 hospitalization demographics.
Cardiovascular diseases emerged as the predominant comorbidity cluster, affecting 47% of patients (hypertension 29.6%, other cardiovascular diseases 16.4%). This finding aligns with Kawatake de Sousa et al.'s observations in Espírito Santo, where cardiovascular conditions (54.37%) and diabetes (19.95%) were leading comorbidities15. The consistency of these patterns across different South American healthcare settings strengthens the evidence for targeted preventive strategies in patients with cardiovascular conditions.
The progressive increase in mortality risk with age and number of NCDs reflects patterns observed in international studies. Our findings particularly reinforce Zhou et al.'s work demonstrating how multiple comorbidities compound COVID-19 severity16. The relationship between chronic diseases and COVID-19 severity appears consistent across healthcare systems, despite variations in resources and population characteristics17,18-20.
The strong association between cardiovascular disease and fatal outcomes supports findings from previous research. A case series of 187 COVID-19 patients found that 27.8% developed myocardial injury, leading to cardiac dysfunction and arrhythmias21. Our observations align with Chen et al.'s findings that cardiac complications occur more frequently in deceased patients, regardless of pre-existing cardiovascular disease22.
The impact of multiple NCDs on COVID-19 outcomes highlights the critical importance of chronic disease prevention and management. As noted by Kluge et al., the true magnitude of at-risk populations may be underestimated, given the high prevalence of undiagnosed hypertension and diabetes in many communities23. This underscores the need for improved NCD screening and management programs.
Our study's primary strength lies in its national representativeness and inclusion of multiple major referral centers. However, data quality variations and incomplete medical records for some variables limited certain analyses. The retrospective nature of the study also precluded collection of some potentially relevant clinical parameters.
These findings emphasize the need for enhanced monitoring of COVID-19 patients with multiple NCDs, particularly those with cardiovascular conditions. Prevention and control of NCDs should be integrated into COVID-19 response strategies, with special attention to older adults with multiple comorbidities.
Prospective studies examining long-term outcomes in COVID-19 survivors with NCDs are needed. Additionally, investigation of regional variations in outcomes and the impact of different treatment protocols on patients with multiple comorbidities would provide valuable insights for healthcare planning.
The impact of COVID-19 countermeasures on NCDs is multifaceted. Physical distancing or quarantine can lead to poor management of behavioral risk factors for NCDs, including unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use, and harmful alcohol use. Evidence from this and previous pandemics suggests that without proper management, chronic conditions may worsen due to stressful situations resulting from restrictions, insecure economic situations, and changes in normal health behaviors23.
Implications for Public Health and Clinical Practice
The strong correlation between multiple NCDs and poor COVID-19 outcomes reinforces the need for preventive measures targeting at-risk groups. These findings support integrating NCD prevention and management into national COVID-19 response strategies, with a particular focus on cardiovascular health. Additionally, the association between advancing age, multiple NCDs, and increased mortality risk mirrors international studies, affirming the compounded vulnerability of older adults with multiple chronic conditions. Proactive monitoring and tailored interventions for such populations could mitigate severe outcomes.
Limitations of the Study
This cross-sectional design provides a snapshot of associations but limits causal interpretations. Due to reliance on available or convenient sampling, generalizability may be limited, and selection bias is possible. Additionally, certain factors, such as the progression of COVID-19 and its interaction with NCDs, cannot be assessed in this design, which restricts our understanding of long-term health impacts. Variability in COVID-19 severity among patients, as well as reliance on self-reported data, introduces further limitations to the robustness of these findings.
Future Research Directions
Prospective studies should examine the long-term health impacts of COVID-19 on patients with NCDs, allowing for better insight into the progression and management of chronic conditions in the context of pandemic-related health challenges. Additionally, research on regional variations and the effectiveness of different treatment protocols for patients with multiple NCDs would contribute valuable data for improving healthcare planning and outcomes. Given the impact of COVID-19 countermeasures on NCD risk factors, future studies should also explore how measures like quarantine influence behavioral risk factors and chronic disease management.
In conclusion, this study underscores the importance of continued research on COVID-19 and NCDs, emphasizing the role of preventative care, the integration of NCD management into pandemic responses, and ongoing publication to inform public health strategies effectively.















